Review Sheet 25 Special Senses Hearing and Equilibrium
1
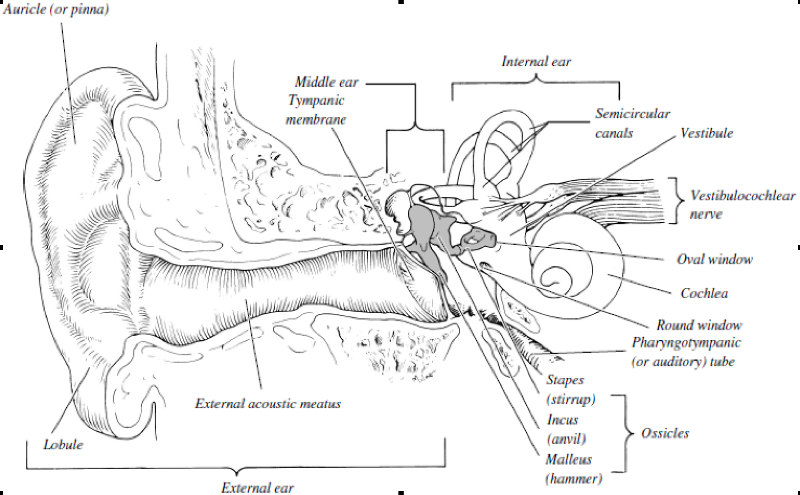
Auricle (pinna)
External acoustic meatus
Tympanic membrane
structures composing the external ear
2
Semicircular canals
Cochlea
Vestibule
structures composing the internal ear
3
Incus (anvil)
Malleus (hammer)
Stapes (stirrup)
collectively called the ossicles
four
Pharyngotympanic (auditory) tube
- involved in equalizing the pressure in the middle ear with atmospheric force per unit area
- passage between the throat and the tympanic cavity
vibrates at the same frequency equally sound waves hitting it; transmits the vibrations to the ossicles
vi
Semicircular canals
Vestibule
contain receptors for the sense of balance
transmits the vibratory motion of the stirrup to the fluid in the scala vestibuli of the internal ear
acts equally a force per unit area relief valve for the increased fluid pressure in the scala tympani; bulges into the tympanic cavity
fluid contained within the membranous labyrinth
fluid contained within the bony labyrinth and bathing the bleary labyrinth
11
- sacs found within the foyer
- sites of the maculae
contains the screw organ
positioned in all spatial planes
pilus cells of the spiral organ remainder on this membrane
gelatinous membrane overlying the hair cells of the spiral organ
contains the crista ampullaris
18
Otoliths, Saccule, Utricle, Vestibular nervus
part in static equilibrium
19
Ampulla, Ampullary cupula, Semicircular ducts, Vestibular nervus
function in dynamic equilibrium
carries auditory information to the encephalon
gelatinous cap overlying hair cells of the crista ampullaris
grains of calcium carbonate in the maculae
23
Trace the pathway through which vibrations are transmitted to stimulate the hair cells in the spiral organ.
Tympanic membrane > malleus > incus > stapes > oval window > perilymph > cochlear duct > endolymph > basilar membrane with pilus cells
24
Describe how sounds of different frequency (pitch) are differentiated in the cochlea.
The frequency determined by the length and tension of the basilar membrane fibers. High pitch sounds = oval window. low pitch = basilar membrane virtually noon of cochlea.
25
Explain the role of the endolymph of the semicircular canals in activating the receptors during athwart motion.
When athwart motility occurs in one direction, the endolymph in a semicircular canal lags behind, pushing the cupula in a direction opposite to that of the angular move. Depending on the ear, this depolarizes or hyperpolarizes the hair cells, resulting in enhanced or reduced impulses to the brain.
26
Explain the role of the otoliths in perception of static equilibrium (caput position).
When the head moves, otoliths move in response to variation in gravitational pull. Every bit the deflect different hair cells, they hyper polarize or depolarize hair cells and modify the rate of impulse transmission along vestibular nerve.
- tin outcome from the fusion of the ossicles
- can issue from impacted cerumen or a perforated eardrum
- can result from a lesion on the cochlear nerve
- sound heard in one ear but not in the other during bone and air conduction
- can effect from a blood jell in the primary auditory cortex
29
Conduction deafness and Sensorineural deafness
- tin result from otitis media
30
The Rinne test evaluates an individual's power to hear sounds conducted by air or bone. Which is more indicative of normal hearing?
involuntary rolling of the optics in any direction or the trailing of the eyes slowly in i direction, followed by rapid middle movement in the contrary management
awareness of dizziness and rotational movement when such motility is not occurring or has ceased
33
The Barany exam investigated the result that rotatory dispatch had on the semicircular canals. Explain why the subject yet had the sensation of rotation immediately after existence stopped.
34
What is the usual reason for conduction the Romberg test?
to determine if impulses are being transmitted upwards the spinal string to the brain properly
35
Wast he degree of sway greater with the optics open up or closed? why?
closed; you lose visual reference points
36
Normal balance, or equilibrium, depends on input from a number of sensory receptors. Proper name them.
vestibular receptors, visual receptors, somatic receptors
37
What consequence does alcohol consumption have on rest and equilibrium? Explain.
alcohol depresses the neurons and enhances the inhibition of coordination and causes a loss of equilibrium reflexes
Source: https://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/37037
0 Response to "Review Sheet 25 Special Senses Hearing and Equilibrium"
Post a Comment